In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, improving efficiency and optimizing production processes are crucial to staying competitive. Two groundbreaking technologies at the forefront of this transformation are edge computing and cloud computing. Individually, they offer unique advantages, but when combined, they create a powerful solution that can revolutionize industrial operations. Let’s explore how these technologies complement each other to enhance efficiency and drive innovation.
Edge Computing
Basics 101
Edge computing refers to the process of data handling at the network’s periphery, close to where data is generated. This reduces latency and enables real-time processing. Unlike cloud computing, where data is processed centrally, edge computing processes data locally, directly on devices or machines.
The Perks of Going Edge
Edge computing brings a bunch of benefits that can really boost the performance and efficiency of production systems. Here are some of the advantages:
- Reduced Latency: Data is processed locally, resulting in faster response times
- Real-Time Processing: Critical applications can be monitored and controlled in real-time
- Lower Bandwidth Usage: Only relevant data is transmitted to the cloud, reducing network load and costs
- Enhanced Data Security: Sensitive information is processed locally, minimizing the need for internet transmission
How It’s Used in Industry
Edge computing plays a vital role in real-time monitoring and local data processing. Machines and equipment can be continuously monitored to assess status and performance, enabling proactive problem-solving. Sensor data processed directly on devices allows for immediate decision-making, enhancing efficiency. Automated processes benefit from faster and more efficient execution, leading to increased productivity.
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing in Simple Terms
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing resources—such as storage, processing power, and networking—over the internet. Instead of investing in and maintaining physical hardware, companies can access these resources on demand from cloud providers.
Cloud services are typically offered in different models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources like servers and storage.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications via the internet, accessible through a browser.
This flexibility allows businesses to scale resources as needed and respond quickly to changing demands.
Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Cloud computing enables companies to scale resources according to demand, avoiding expensive hardware investments. Key benefits include:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models reduce operational costs and improve budget planning.
- Flexibility: Cloud services are accessible from anywhere, facilitating not only the use of tools but also access to data and analytics results.
- Improved Collaboration: Centralized data storage enhances teamwork and information sharing. Real-time access to shared resources allows teams to collaborate more efficiently, regardless of location, driving productivity and innovation.
- Enhanced Data Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security technologies such as encryption, access controls and continuous monitoring. However, security is a shared responsibility—customers must also implement appropriate safeguards for their data and applications.
Cloud Computing in Action
In industrial settings, cloud computing, is used for storing and analyzing large datasets, providing valuable insights into production processes and enhancing efficiency. Remote monitoring of machines and equipment allows for early problem detection and timely maintenance. Sensor data analysis identifies potential issues and enables preventive measures, reducing downtime. Cloud-based solutions improve supply chain planning and management, preventing bottlenecks and boosting efficiency.
The Power of Combining Edge and Cloud Computing
Synergies and Collaboration
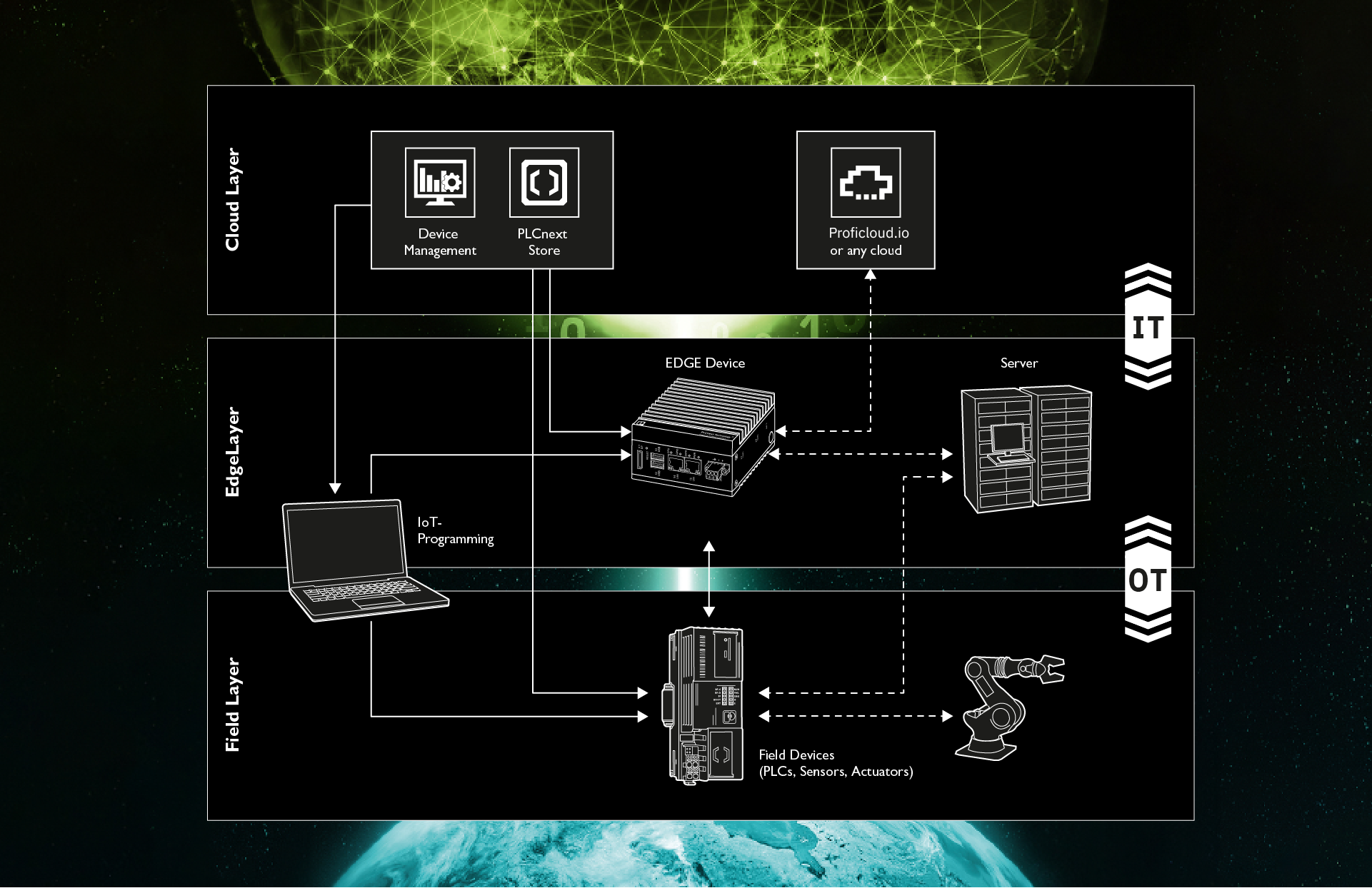
Edge and cloud computing form a perfect partnership. Edge computing allows fast and efficient on-site data processing, while the cloud provides extensive computing power and storage. By combining these technologies, companies can maximize the benefits of both approaches and optimize their production processes.
Hybrid Architectures: The Perfect Match
Hybrid architectures integrate the strengths of edge and cloud computing to ensure optimal resource utilization. In a hybrid environment, data is processed locally, and only essential information is transmitted to the cloud. This approach enhances resource efficiency and application performance.
A practical example of a hybrid architecture involves processing sensor data directly on machines (edge computing) for immediate decision-making and efficiency improvements. Simultaneously, critical data is sent to the cloud for comprehensive analysis and long-term storage. This combination leverages real-time processing and extensive analytical capabilities without overloading the network.
Conclusion
Edge and cloud computing are not competing technologies – they complement each other. By leveraging both approaches, companies can maximize the benefits of each technology, making their production processes more efficient and secure. The future of industry lies in the intelligent combination of edge and cloud computing, addressing modern production challenges and driving innovative solutions.
Wait a minute! What’s behind Smart Services?
Phoenix Contact offers a range of Smart Services powered by Proficloud.io, specifically designed to enhance efficiency and productivity in the industrial sector. These Smart Services leverage the advantages of cloud computing to provide businesses with flexible, scalable and cost-effective solutions.
By utilizing data analytics, monitoring and management, these Smart Services enable companies to gain deeper insights into their operations, detect anomalies early and make data-driven decisions. This leads to optimized production processes, reduced downtime and improved overall performance.
By delivering secure and reliable solutions, these Smart Services help companies stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Cloud computing is a key component of modern industry and will continue to play a central role in the development of innovative solutions.





